Vandals

The Vandals were an East Germanic tribe that entered the late Roman Empire during the 5th century, perhaps best known for their sack of Rome in 455. Although they were not notably more destructive than other invaders of ancient times, Renaissance and Early Modern writers who idealized Rome tended to blame the Vandals for its destruction. This led to the coinage of "vandalism", meaning senseless destruction, particularly the defacing of artworks that were completed with great effort.
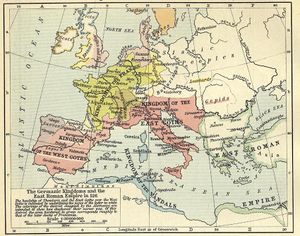
The Goth leader Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths and regent of the Visigoths, was allied by marriage with the Vandals as well as with the Burgundians and the Franks under Clovis I. Like the Goths, the Vandals, whose influence can best be judged in their longest-lasting kingdom in North Africa, were continuators rather than violaters of Roman culture in Late Antiquity.[1]
Contents |
Etymology and modern use
In modern usage, a "vandal" is someone who engages in senseless destruction. This usage is a result of the Vandals' sack of Rome under King Genseric in 455. The Vandals may not have been any more destructive than other invaders of ancient times, but writers who idealized Rome often blamed them for its destruction. For example, British Enlightenment poet John Dryden wrote, Till Goths, and Vandals, a rude Northern race,/ Did all the matchless Monuments deface.[2]
The term Vandalisme was coined in 1794 by Henri Grégoire, bishop of Blois, to describe the destruction of artwork following the French Revolution. The term was quickly adopted across Europe. This new use of the term was important in colouring the perception of the Vandals from later Late Antiquity, popularising the pre-existing idea that they were a barbaric group with a taste for destruction. Vandals and other "barbarian" groups had long been blamed for the fall of the Roman Empire by writers and historians.[3]
From around 1540, the Swedish king had been styled, Suecorum, Gothorum et Vandalorum Rex: King of the Swedes, Goths and Vendes.[4] Carl XVI Gustaf, dropped the title in 1973 and now styles himself simply as King of Sweden.
Origins and early history
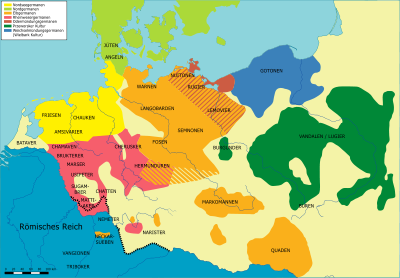
Some archaeologists and historians identify the Vandals with the Przeworsk culture, and controversy surrounds potential connections between the Vandals and another, possibly a mixture of Slavic and Germanic tribes, the Lugii (Lygier, Lugier or Lygians), which is referred to as inhabiting the area by Roman writers. Some academics believe that either Lugii was an earlier name of the Vandals, or the Vandals were part of the Lugian federation, which was composed of Germanic and Slavic tribes. Jordanes refers to Vandals as Gothic (East Germanic) speakers, and name etymologies support the notion of Vandalic being near related to Gothic. The bearers of the Przeworsk culture (possibly the Lugii) had the custom of cremation. Cremation is characteristic to Baltic Prussian tribes. In Prussia both cremation and inhumation burials were found, which Germanic tribes practised. The remains of the Przeworsk culture is mainly traced in the areas which were marshes, when Romans mentioned the Lugii tribe.
Similarities of names have led to appointing homelands for the Vandals in Norway (Hallingdal), Sweden (Vendel), or Denmark (Vendsyssel). The Vandals are assumed to have crossed the Baltic into what is today Poland somewhere in the 2nd century BC, and to have settled in Silesia from around 120 BC. This tradition supports the identification of the Vandals with the Przeworsk culture, since the Gothic Wielbark culture seems to have replaced a branch of that culture.
Some Medieval authors applied the ethnonym "Vandals" to Slavic peoples: Wends, Lusatians or Poles.[5][6][7]
Introduction into the Roman Empire
The Vandals were divided in two tribal groups, the Silingi and the Hasdingi. At the time of the Marcomannic Wars (166–180) the Silingi lived in an area recorded by Tacitus as Magna Germania. In the 2nd century, the Hasdingi, led by the kings Raus and Rapt (or Rhaus and Raptus) moved south, and first attacked the Romans in the lower Danube area. In about 271 the Roman Emperor Aurelian was obliged to protect the middle course of the Danube against them. They made peace and settled in western Dacia and Pannonia.

According to Jordanes' Getica, the Hasdingi came into conflict with the Goths around the time of Constantine the Great. At the time, the Vandals were living in lands later inhabited by the Gepids, where they were surrounded "on the east [by] the Goths, on the west [by] the Marcomanni, on the north [by] the Hermanduri and on the south [by] the Hister (Danube)." The Vandals were attacked by the Gothic king Geberic, and their king Visimar was killed. The Vandals then migrated to Pannonia, where after Constantine the Great (about 330) granted them lands on the right bank of the Danube, they lived for the next sixty years.
Around this time, the Hasdingi had already been Christianized. During the Emperor Valens's reign (364–78) the Vandals accepted, much like the Goths earlier, Arianism, a belief that was in opposition to that of Nicene orthodoxy of the Roman Empire. Yet there were also some scattered orthodox Vandals, among whom was the famous magister militum Stilicho, the chief minister of the Emperor Honorius.
In 400 or 401, possibly because of attacks by the Huns, the Vandals, under king Godigisel, along with their allies (the Sarmatian Alans and Germanic Suebians) moved westwards into Roman territory. Some of the Silingi joined them later. Vandals raided the Roman province of Raetia in the winter of 401/402. From this, historian Peter Heather concludes that at this time the Vandals were located in the region around the Middle and Upper Danube.[8]
In Gaul
In 406 the Vandals advanced from Pannonia travelling west along the Danube without much difficulty, but when they reached the Rhine, they met resistance from the Franks, who populated and controlled Romanized regions in northern Gaul. Twenty thousand Vandals, including Godigisel himself, died in the resulting battle, but then with the help of the Alans they managed to defeat the Franks, and on December 31, 406 the Vandals crossed the Rhine to invade Gaul, which they devastated terribly. Under Godigisel's son Gunderic, the Vandals plundered their way westward and southward through Aquitaine.
In Hispania
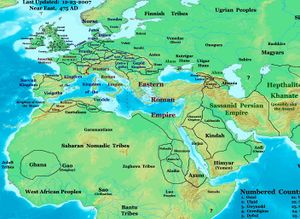
On October 13, 409 they crossed the Pyrenees into the Iberian peninsula. There, the Hasdingi received land from the Romans, as foederati, in Gallaecia (Northwest) and the Silingi in Hispania Baetica (South), while the Alans got lands in Lusitania (West) and the region around Carthago Nova. The Suebi also controlled part of Gallaecia. The Visigoths, who invaded Iberia before receiving lands in Septimania (Southern France), crushed the Alans in 426, killing the western Alan king Attaces. The remainder of his people subsequently appealed to the Vandal king Gunderic to accept the Alan crown. Later Vandal kings in North Africa styled themselves Rex Wandalorum et Alanorum ("King of the Vandals and Alans").
The Arabic term for Muslim Iberia Al Andalus, and its derivative Andalusia, may be derived from the Berber pronunciation of Vandal: "Wandal". However, the theory has been disputed, and alternative etymologies for Andalusia have been proposed.[9][10]
The Vandal Kingdom in North Africa
Establishment

The Vandals under their new king Genseric (also known as Geiseric) crossed to Africa in 429.[11] Although numbers are unknown and some historians debate the validity of estimates, based on Procopius' assertion that the Vandals and Alans numbered 80,000 when they moved to North Africa,[12] Heather estimates that they could have fielded an army of around 15,000–20,000.[13] According to Procopius, the Vandals came to Africa at the request of Boniface, the military ruler of the region.[14] However, it has been suggested that the Vandals migrated to Africa in search of safety; they had been attacked by a Roman army in 422 and had failed to seal a treaty with them. Advancing eastwards along the coast, the Vandals lay siege to Hippo Regius in 430.[11] Inside Saint Augustine and his priests prayed for relief from the invaders, knowing full well that the fall of the city would spell conversion or death for many Roman Christians. On 28 August 430, three months into the siege, St. Augustine (who was 75 years old) died,[15] perhaps from starvation or stress, as the wheat fields outside the city lay dormant and unharvested. After 14 months, hunger and the inevitable diseases were ravaging both the city inhabitants and the Vandals outside the city walls.
Peace was made between the Romans and the Vandals in 435 through a treaty giving the Vandals control of coastal Numidia. Geiseric chose to break the treaty in 439 when he invaded the province of Africa Proconsularis and laid siege to Carthage.[16] The city was captured without a fight; the Vandals entered the city while most of the inhabitants were attending the races at the hippodrome. Genseric made it his capital, and styled himself the King of the Vandals and Alans, to denote the inclusion of the Alans of northern Africa into his alliance. Conquering Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica and the Balearic Islands, he built his kingdom into a powerful state. Historian Camerson suggests that the new Vandal rule may not have been unwelcomed by the population of North Africa as the previous landowners were generally unpopular.[17]
The impression given by ancient sources such as Victor of Vita, Quodvultdeus, and Fulgentius of Ruspe was that the Vandal take-over of Carthage and North Africa led to widespread destruction. However, recent archaeological investigations have challenged this assertion. Although Carthage's Odeon was destroyed, the street pattern remained the same and some public buildings were renovated. The political centre of Carthage was the Byrsa Hill. New industrial centres emerged within towns during this period.[18] Historian Andy Merrills uses the large amounts of African Red Slip ware discovered across the Mediterranean dating from the Vandal period of North Africa to challenge the assumption that the Vandal rule of North Africa was a time of economic instability.[19] The Vandals raided Sicily in 440, however the Western Roman Empire was too preoccupied with war with Gaul to react. Theodosius II, emperor of the Eastern Roman Empire, dispatched an expedition to deal with the Vandals in 441, however it only progressed as far as Sicily. The Western Empire under Valentinian III secured peace with the Vandals in 442.[20] Under the treaty the Vandals gained Byzacena, Tripolitania, part of Numidia, and confirmed their control of Proconsular Africa.[21]
Sack of Rome
During the next thirty-five years, with a large fleet, Genseric looted the coasts of the Eastern and Western Empires. After Attila the Hun's death, however, the Romans could afford to turn their attention back to the Vandals, who were in control of some of the richest lands of their former empire.
In an effort to bring the Vandals into the fold of the Empire, Valentinian III offered his daughter's hand in marriage to Genseric's son. Before this "treaty" could be carried out, however, politics again played a crucial part in the blunders of Rome. Petronius Maximus, the usurper, killed Valentinian III in an effort to control the Empire. Diplomacy between the two factions broke down, and in 455 with a letter from the Empress Licinia Eudoxia, begging Genseric's son to rescue her, the Vandals took Rome, along with the Empress Licinia Eudoxia and her daughters Eudocia and Placidia.
The chronicler Prosper of Aquitaine[22] offers the only fifth-century report that on 2 June 455, Pope Leo the Great received Genseric and implored him to abstain from murder and destruction by fire, and to be satisfied with pillage. Whether the pope's influence saved Rome is, however, questioned. The Vandals departed with countless valuables, including the spoils of the Temple in Jerusalem booty brought to Rome by Titus. Eudoxia and her daughter Eudocia were taken to North Africa.[21]
Consolidation
As a result of the Vandal sack of Rome and piracy in the Mediterranean, it became important to the Roman Empire to destroy the Vandal kingdom. the first retaliation was in 460, when both Western and Eastern empires sent fleets against the Vandals. The Vandals captured the Western fleet, and destroyed the Eastern through the use of fire ships.[20] Following up the attack, the Vandals tried to invade the Peloponnese but were driven back by the Maniots at Kenipolis with heavy losses.[23] In retaliation, the Vandals took 500 hostages at Zakynthos, hacked them to pieces and threw the pieces overboard on the way to Carthage.[23] In the 470s, the Romans abandoned their policy of war against the Vandals. The Western general Ricimer reached a treaty with the Vandals,[20] and in 476 Genseric was able to conclude a "perpetual peace" with Constantinople. Relations between the two states assumed a veneer of normality.[24] From 477 onwards, the Vandals produced their own coinage. It was restricted to bronze and silver low-denomination coins. Although the low-denomination imperial money was replaced, the high-denomination was not, demonstrating in the words of Merrills "reluctance to usurp the imperial prerogative".[25]
Although the Vandals had fended off attacks from the Romans and established hegemony over the islands of the western Mediterranean, they were less successful in their conflict with the Berbers. Situated south of the Vandal kingdom, the Berbers inflicted two major defeats on the Vandals in the period 496–530[20]
Domestic religious tensions
Differences between the Arian Vandals and their Trinitarian subjects (including both Catholics and Donatists) were a constant source of tension in their African state. Catholic bishops were exiled or killed by Genseric and laymen were excluded from office and frequently suffered confiscation of their property.[26] He protected his Catholic subjects when his relations with Rome and Constantinople were friendly, as during the years 454–57, when the Catholic community at Carthage, being without a head, elected Deogratias bishop. The same was also the case during the years 476–477 when Bishop Victor of Cartenna sent him, during a period of peace, a sharp refutation of Arianism and suffered no punishment. Huneric, Genseric's successor, issued edicts against Catholics in 483 and 484 in an effort to marginalise them and make Arianism the primary religion in North Africa.[27] Generally most Vandal kings, except Hilderic, persecuted Trinitarian Christians to a greater or lesser extent, banning conversion for Vandals, exiling bishops and generally making life difficult for Trinitarians.
Decline
According to the 1913 Catholic Encyclopedia: "Genseric, one of the most powerful personalities of the "era of the Migrations", died on 25 January 477, at the great age of around 88 years. According to the law of succession which he had promulgated, the oldest male member of the royal house was to succeed. Thus he was succeeded by his son Huneric (477–484), who at first tolerated Catholics, owing to his fear of Constantinople, but after 482 began to persecute Manichaeans and Catholics."[28]
Gunthamund (484 – 496), his cousin and successor, sought internal peace with the Catholics and ceased persecution once more. Externally, the Vandal power had been declining since Genseric's death, and Gunthamund lost large parts of Sicily to the Ostrogoths and had to withstand increasing pressure from the autochthonous Moors.
According to the 1913 Catholic Encyclopedia: "While Thrasamund (496–523), owing to his religious fanaticism, was hostile to Catholics, he contented himself with bloodless persecutions".[28]
The turbulent end
Hilderic (523 – 530) was the Vandal king most tolerant towards the Catholic Church. He granted it religious freedom; consequently Catholic synods were once more held in North Africa. However, he had little interest in war, and left it to a family member, Hoamer. When Hoamer suffered a defeat against the Moors, the Arian faction within the royal family led a revolt, raising the banner of national Arianism, and his cousin Gelimer (530 – 533) became king. Hilderic, Hoamer and their relatives were thrown into prison. Hilderic was deposed and murdered in 533.[29]
Byzantine Emperor Justinian I declared war, with the stated intention of restoring Huneric to the Vandal throne. While an expedition was en route, a large part of the Vandal army and navy was led by Tzazo, Gelimer's brother, to Sardinia to deal with a rebellion. As a result, the armies of the Eastern Empire commanded by Belisarius were able to land unopposed 10 miles (16 km) from Carthage. Gelimer quickly assembled an army,[30] and met Belisarius at the Battle of Ad Decimum; the Vandals were winning the battle until Gelimer's brother Ammatas and nephew Gibamund fell in battle. Gelimer then lost heart and fled. Belisarius quickly took Carthage while the surviving Vandals fought on.[31]
On December 15, 533, Gelimer and Belisarius clashed again at the Battle of Tricamarum, some 20 miles (32 km) from Carthage. Again, the Vandals fought well but broke, this time when Gelimer's brother Tzazo fell in battle. Belisarius quickly advanced to Hippo, second city of the Vandal Kingdom, and in 534 Gelimer surrendered to the Roman conqueror, ending the Kingdom of the Vandals.
North Africa (which is north Tunisia and eastern Algeria at the period of the vandal) became a Roman province again, from which the Vandals were expelled. The most part of the Vandals went to Saldae (which is called today Béjaïa in the Kabyl land in north Algeria) where they integrated the Berbers. Some other were put into imperial service or fled to the two Gothic kingdoms (Ostrogothic Kingdom and Visigothic kingdom), some vandal women married Byzantine soldiers settled in north Algeria and Tunisia. The choicest Vandal warriors were formed into five cavalry regiments, known as Vandali Iustiniani, and stationed on the Persian frontier. Some entered the private service of Belisarius.[32] The 1913 Catholic Encyclopedia states that "Gelimer was honourably treated and received large estates in Galatia. He was also offered the rank of a patrician but had to refuse it because he was not willing to change his Arian faith".[28] In the words of historian Roger Collins: "The remaining Vandals were then shipped back to Constantinople to be absorbed into the imperial army. As a distinct ethnic unit they disappeared".[30]
Kings
- Wisimar (d.335)
- Godigisel (359–406)
- Gunderic (407–428)
- Genseric (428–477)
- Huneric (477–484)
- Gunthamund (484–496)
- Thrasamund (496–523)
- Hilderic (523–530)
- Gelimer (530–534)
Culture
Very little is known about the Vandalic language itself, which was of the East Germanic linguistic branch. The Goths left behind the only known example of the East Germanic language type: a 4th-century translation of the Gospels.[33] All Vandals that modern historians know about spoke Latin, which also remained the official language of the Vandal administration (most of the staff seems to have been native African/Roman).[34] Levels of literacy in the ancient world are uncertain, but writing was integral to administration and business. Studies of literacy in North Africa have tended to centre around the administration, which was limited to the social elite. However, the majority of the population of North Africa did not live in urban centres.[35]
Judith George explains that "Analysis of the [Vandal] poems in their context holds up a mirror to the ways and values of the times".[36] Very little work of the poets of Vandal North Africa survives, but what does is found in the Latin Anthology; apart from their names, little is known about the poets themselves, not even when they were writing. Their work drew on earlier Roman traditions. Modern scholars have generally hold the view that the Vandals allowed the Romans in North Africa to carry on with their way of life with only occasional interference.[37]
See also
- Auriwandalo
- Migrations period
- Timeline of Germanic kingdoms
- Vistula Veneti
- Wanda
- Wendel
References
- Bibliography
- Burke, Ulick Ralph (1900), A History of Spain from the Earliest Times to the Death of Ferdinand the Catholic, Year Books, ISBN 9781443740548, http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=DuiyyWGg-KEC&dq=A+History+of+Spain+from+the+Earliest+Times+to+the+Death+of+Ferdinand+the+Catholic&source=gbs_navlinks_s
- Bury, John Bagnell (1923), History of the Later Roman Empire, from the Death of Theodosius I to the Death of Justinian (A.D.395 to A.D. 565). Volume II, Macmillan, http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/secondary/BURLAT/home.html
- Cameron, Averil (2000), "The Vandal conquest and Vandal rule (A.D. 429–534)", XIV, Cambridge University Press, pp. 553–559
- Collins, Roger (2000), "Vandal Africa, 429–533", XIV, Cambridge University Press, pp. 124–126
- Conant, Jonathan (2004), "Literacy and Private Documentation in Vandal North Africa: The Case of the Albertini Tablets", Vandals, Romans and Berbers: New Perspectives on Late Antique North Africa, Ashgate Publishing, pp. 199–224, ISBN 0-7546-4145-7, http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=xdnrTM_d1GkC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Vandals&hl=en&ei=uKjUS-OzCeihOOOSoY4O&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDUQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false
- George, Judith (2004), "Vandal Poets in their Context", Vandals, Romans and Berbers: New Perspectives on Late Antique North Africa, Ashgate Publishing, pp. 133–144, ISBN 0-7546-4145-7, http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=xdnrTM_d1GkC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Vandals&hl=en&ei=uKjUS-OzCeihOOOSoY4O&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDUQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false
- Greenhalgh, P. A. L.; Eliopoulos, Edward (1985), Deep into Mani: Journey to the Southern Tip of Greece, Faber and Faber, ISBN 9780571135233
- Heather, Peter (2005), The Fall of the Roman Empire: A New History, Macmillan, ISBN 0-333-98914-7
- Mallory, James P.; Adams, Douglas Q. (eds) (1997), Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 1-884964-98-2, http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=tzU3RIV2BWIC&dq=Encyclopedia+of+Indo-European+Culture&source=gbs_navlinks_s
- Merrills, Andy (2004), "Vandals, Romans and Berbers: Understanding Late Antique North Africa", Vandals, Romans and Berbers: New Perspectives on Late Antique North Africa, Ashgate Publishing, pp. 3–28, ISBN 0-7546-4145-7, http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=xdnrTM_d1GkC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Vandals&hl=en&ei=uKjUS-OzCeihOOOSoY4O&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDUQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=false
- Merrills, Andy; Miles, Richard (2010), The Vandals, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-1-4051-6068-1, http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=yTIHPoyMOFYC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Vandals&hl=en&ei=uKjUS-OzCeihOOOSoY4O&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=2&ved=0CDoQ6AEwAQ#v=onepage&q&f=false
- Mokhtar, G (1981), Ancient Civilizations of Africa, University of California Press, ISBN 0520066979
- Wickham, Chris (2009), The Inheritance of Rome, Penguin Books, ISBN 978-0-670-02098-0
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed (1913). "Vandals". Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed (1913). "Vandals". Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company.
- Notes
- ↑ Contrasting articles in Frank M. Clover and R.S. Humphreys, eds, Tradition and Innovation in Late Antiquity (University of Wisconsin Press) 1989, highlight the Vandals' role as continuators: Frank Clover stresses continuities in North African Roman mosaics and coinage and literature, whereas Averil Cameron, drawing upon archaeology, documents how swift were the social, religious and linguistic changes once the area was conquered by Byzantium and then Islam.
- ↑ Dryden, John, "To Sir Godfrey Kneller", 1694. Dryden also wrote But Italy, reviving from the trance/Of Vandal, Goth and Monkish ignorance. (1680).
- ↑ Merrills & Miles 2010, pp. 9–10
- ↑ Merrills & Miles 2010, p. 9
- ↑ Annales Alamannici, 795 ad
- ↑ Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum by Adam Bremensis 1075 ad
- ↑ Roland Steinacher under Reiner Protsch"Studien zur vandalischen Geschichte. Die Gleichsetzung der Ethnonyme Wenden, Slawen und Vandalen vom Mittelalter bis ins 18. Jahrhundert", 2002
- ↑ Heather 2005, p. 195
- ↑ Mokhtar 1981, p. 281
- ↑ Burke 1900, p. 410
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Collins 2000, p. 124
- ↑ Procopius Wars 3.5.18–19 in Heather 2005, p. 512
- ↑ Heather 2005, pp. 197–198
- ↑ Procopius Wars 3.5.23–24 in Collins 2004, p. 124
- ↑ Newadvent.org
- ↑ Collins 2004, pp. 124–125
- ↑ Cameron 2000, pp. 553–554
- ↑ Merrills 2004, p. 10
- ↑ Merrills 2004, p. 11
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 Collins 2000, p. 125
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Cameron 2000, p. 553
- ↑ Prosper's account of the event was followed by his continuator in the sixth century, Victor of Tunnuna, a great admirer of Leo quite willing to adjust a date or bend a point (Steven Muhlberger, "Prosper's Epitoma Chronicon: was there an edition of 443?" Classical Philology 81.3 (July 1986), pp 240-244).
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 21
- ↑ Bury 1923, p. 125
- ↑ Merrills 2004, pp. 11–12
- ↑ Collins 2004, pp. 125–126
- ↑ Cameron 2000, p. 555
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 Catholic Encyclopedia 1913, "Vandals".
- ↑ Bury 1923, p. 131
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Collins 2004, p. 126
- ↑ Bury 1923, pp. 133–135
- ↑ Bury 1923, pp. 124–150
- ↑ Mallory & Adams 1997, pp. 217, 301
- ↑ Wickham 2009, p. 77
- ↑ Conant 2004, pp. 199–200
- ↑ George 2004, p. 138
- ↑ George 2004, pp. 138–139
Further reading
- Blume, Mary. "Vandals Exhibit Sacks Some Cultural Myths", International Herald Tribune, August 25, 2001.
- Christian Courtois: Les Vandales et l'Afrique. Paris 1955
- Clover, Frank M: The Late Roman West and the Vandals. Aldershot 1993 (Collected studies series 401), ISBN 0-86078-354-
- Die Vandalen: die Könige, die Eliten, die Krieger, die Handwerker. Publikation zur Ausstellung "Die Vandalen"; eine Ausstellung der Maria-Curie-Sklodowska-Universität Lublin und des Landesmuseums Zamość ...; Ausstellung im Weserrenaissance-Schloss Bevern... Nordstemmen 2003. ISBN 3-9805898-6-2
- John Julius Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries
- F. Papencordt’s Geschichte der vandalischen Herrschaft in Afrika
- Guido M. Berndt, Konflikt und Anpassung: Studien zu Migration und Ethnogenese der Vandalen (Historische Studien 489, Husum 2007), ISBN 978-3-7868-1489-4.
- Hans-Joachim Diesner: Vandalen. In: Paulys Realencyclopädie der class. Altertumswissenschaft (RE Suppl. X, 1965), S. 957-992.
- Hans-Joachim Diesner: Das Vandalenreich. Aufstieg und Untergang. Stuttgart 1966. 5.
- Helmut Castritius: Die Vandalen. Etappen einer Spurensuche. Stuttgart u.a. 2007.
- Ivor J. Davidson, A Public Faith, Chapter 11, Christians and Barbarians, Volume 2 of Baker History of the Church, 2005, ISBN 0-8010-1275-9
- L’Afrique vandale et Byzantine. Teil 1. Turnhout 2002 (Antiquité Tardive 10), ISBN 2-503-51275-5.
- L’Afrique vandale et Byzantine. Teil 2, Turnhout 2003 (Antiquité Tardive 11), ISBN 2-503-52262-9.
- Lord Mahon Philip Henry Stanhope, 5th Earl Stanhope, The Life of Belisarius, 1848. Reprinted 2006 (unabridged with editorial comments) Evolution Publishing, ISBN 1-889758-67-1. Evolpub.com
- Ludwig Schmidt: Geschichte der Wandalen. 2. Auflage, München 1942.
- Pauly-Wissowa
- Pierre Courcelle: Histoire littéraire des grandes invasions germaniques. 3rd edition Paris 1964 (Collection des études Augustiniennes: Série antiquité, 19).
- Roland Steinacher: Vandalen - Rezeptions- und Wissenschaftsgeschichte. In: Hubert Cancik (Hrsg.): Der Neue Pauly, Stuttgart 2003, Band 15/3, S. 942-946, ISBN 3-476-01489-4.
- Roland Steinacher: Wenden, Slawen, Vandalen. Eine frühmittelalterliche pseudologische Gleichsetzung und ihr Nachleben bis ins 18. Jahrhundert. In: W. Pohl (Hrsg.): Auf der Suche nach den Ursprüngen. Von der Bedeutung des frühen Mittelalters (Forschungen zur Geschichte des Mittelalters 8), Wien 2004, S. 329-353. Uibk.ac.at
- Stefan Donecker; Roland Steinacher, Rex Vandalorum - The Debates on Wends and Vandals in Swedish Humanism as an Indicator for Early Modern Patterns of Ethnic Perception, in: ed. Robert Nedoma, Der Norden im Ausland - das Ausland im Norden. Formung und Transformation von Konzepten und Bildern des Anderen vom Mittelalter bis heute (Wiener Studien zur Skandinavistik 15, Wien 2006) 242-252. Uibk.ac.at
- Victor of Vita, History of the Vandal Persecution ISBN 0-85323-127-3. Written 484.
- Walter Pohl: Die Völkerwanderung. Eroberung und Integration. Stuttgart 2002, S. 70-86, ISBN 3-17-015566-0.
- Westermann, Grosser Atlas zur Weltgeschichte (German)
- Yves Modéran: Les Maures et l'Afrique romaine. 4e.-7e. siècle. Rom 2003 (Bibliothèque des Écoles françaises d'Athènes et de Rome, 314), ISBN 2-7283-0640-0.
External links
![]() "Vandals" in the 1913 Catholic Encyclopedia.
"Vandals" in the 1913 Catholic Encyclopedia.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
